24-Month data
Proven with 2 years of data,
IZERVAY continued to slow lesion growth through 24 months and demonstrated an increasing treatment effect7
The annualized rate of GA growth (MMRM analysis)§ at 24 months in GATHER27
IZERVAY 2 mg EM
- 2.23 mm2/year
- 14% reduction at 24 months; difference vs sham (95% CI) mm2/year||=0.36 (0.07-0.66); p=0.0165
IZERVAY 2 mg EM to EOM
- 2.10 mm2/year
- Due to the hierarchical testing procedure, no statistical test was performed for the EOM treatment group
The recommended dose for IZERVAY is 2 mg once monthly (approximately 28 ± 7 days)7
§Non-transformed GA growth slope analysis.
||Percent difference is calculated by 100×(difference)/(least squares mean from sham).
Trial design: The efficacy and safety of IZERVAY were demonstrated in 2 randomized, multicenter, double-masked, sham-controlled, 18-month and 24-month studies in patients with GA due to AMD. The primary endpoint evaluated the mean rate of GA growth (slope) from baseline to Month 12, measured by fundus autofluorescence (FAF) at 3 time points (baseline, Month 6, and Month 12). In GATHER2, the mean rate of GA growth (slope) measured by FAF was evaluated at 2 additional time points (Month 18 and Month 24).7
Post hoc data
In a post hoc analysis,
Fewer IZERVAY patients lost their driving eligibility compared to sham14
Driving vision threshold of 20/40 at or up to 12 months
In a pooled post hoc analysis of the GATHER trials, fewer patients on IZERVAY fell below the driving vision threshold of 20/40 at or up to 12 months compared to sham.
The absolute low vision BCVA cutoff varies by state in the United States. The cutoff for loss of legal driving vision in this post hoc analysis was eyes with a baseline of ≥70 letters (20/40) that progressed to ≤60 letters (20/63) at or up to Month 12. Persistent loss of driving vision was defined as patients who progressed to ≤60 letters at 2 consecutive post-baseline visits.
- There are a number of factors that determine a patient's ability to drive and this decision should be considered carefully by each patient and their doctor
- Given the exploratory post hoc nature of the data, these results should be interpreted with caution and cannot be considered conclusive
In a post hoc analysis over 12 months,
IZERVAY signaled a 56% reduction in patients' risk of vision loss compared to sham14
Persistent vision loss in this pooled analysis from the GATHER clinical trials was defined as a loss of ≥15 letters (ETDRS) in BCVA from baseline measured at any 2 consecutive visits up to Month 12, with a 56% risk reduction in persistent vision loss with IZERVAY vs sham.
- Masked image and adverse event analysis completed to further ensure vision loss was consistent with disease progression
- Given the exploratory post hoc nature of the data, these results should be interpreted with caution and cannot be considered conclusive
Trial design
IZERVAY was evaluated in patients with GA secondary to AMD7

Baseline patient demographics15,16
Baseline characteristics were balanced across trials and treatment arms
Scroll left to view more.
|
GATHER1
IZERVAY
(n=67)
|
GATHER1
Sham
(n=110)
|
GATHER2
IZERVAY
(n=225)
|
GATHER2
Sham
(n=222)
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years GATHER1: mean (SD); GATHER2: median (IQR) |
78.8 (10.2) | 78.2 (8.8) | 77 (71-83) | 77 (71-83) |
| Female, n (%) | 45 (67.2) | 79 (71.8) | 154 (68) | 156 (70) |
| Caucasian, n (%) | 67 (100) | 107 (97.3) | 182 (81) | 186 (84) |
| Active smoker, n (%) | 25 (37.3) | 36 (32.7) | 106 (47) | 107 (48) |
| Mean total GA area, mm2 (SD)# | 7.33 (3.79) | 7.42 (3.84) | 7.48 (4.00) | 7.81 (3.89) |
| Mean square root GA area, mm2 (SD)# | 2.62 (0.70) | 2.63 (0.70) | 2.64 (0.71) | 2.71 (0.70) |
| Bilateral GA, n (%) | 67 (100) | 108 (98.2) | 212 (94) | 210 (95) |
| Mean BCVA, letters (SD)# | 70.2 (10.0) | 69.0 (10.4) | 70.9 (8.9) | 71.6 (9.4) |
| Mean LL-BCVA letters (SD)# | 36.7 (21.1) | 34.5 (19.3) | 41.0 (19.7) | 39.6 (19.6) |
Around 84% of patients had disease within 500 μm of the foveal center point1
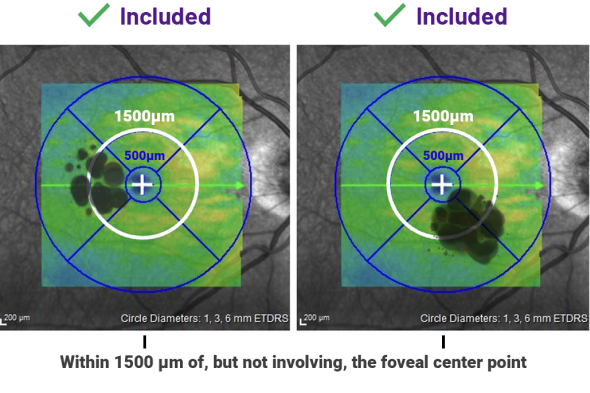
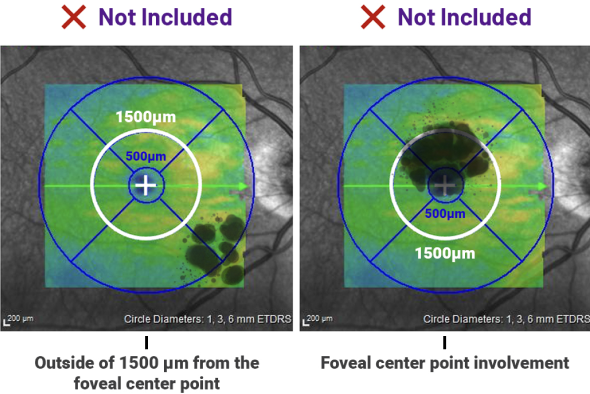
Additional inclusion criteria16,17
- ≥50 years
- BCVA between 20/25 and 20/320
- GA lesions:
- Total area between 2.5 mm2 and 17.5 mm2 (1-7 DA, respectively)
- If multifocal lesions, at least 1 lesion had to be ≥1.25 mm2 (0.5 DA)
Additional exclusion criteria16,17
- Evidence of choroidal neovascularization (CNV) or any sign of diabetic retinopathy in either eye at baseline
- GA secondary to any condition other than AMD in either eye
- Any prior treatment for AMD or any prior intravitreal treatment for any indication in either eye (except oral vitamin or mineral supplements)
- Any ocular condition in study eye that could progress during the study and potentially affect central vision or otherwise act as a confounding factor
AMD=age-related macular degeneration; BCVA=best corrected visual acuity; CI=confidence interval; DA=disc area; EM=every month; EOM=every other month; ETDRS=Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study; GA=geographic atrophy; IQR=interquartile range; LL-BCVA=low-luminance BCVA; MMRM=mixed models for repeated measures; SD=standard deviation.